![[VIDEO] Ultrasound-Guided Injection for Trigger Finger](https://drjordijimenez.com/imagen/100/100/Imagenes/infiltracion-ecoguidada-dedo-resorte-drjordijimenez.jpg)
- Home /
- EXERCISES /
- SHOULDER EXERCISES /
- EXERCISE FOR SUPRASPINAUS TEAR
EXERCISE FOR SUPRASPINAUS TEAR
Stretching and Strengthening Exercises for Supraspinatus Tear
In recent years, it has become clear that rotator cuff tears, although they can be progressive, often progress slowly and without significant symptoms. This has influenced the way doctors approach their treatment, opting in most cases for a conservative approach.
Conservative treatment, which focuses on pain management and exercise rehabilitation, has been shown to be as effective as surgery for many patients, especially older patients with atraumatic tears. Exercises are a key component of this treatment and are designed to improve shoulder joint mobility and strengthen the surrounding muscles, such as the rotator cuff muscles and the muscles that attach the scapula. These exercises should begin at a low intensity and gradually increase, as long as they do not cause significant pain.
For this type of treatment to be effective, certain criteria must be met:
- Rule out the existence of other serious pathologies or causes of pain.
- Pain that is persistent (more than three months) or recurring, but not severe. If the pain is severe, measures should be taken to relieve it first.
- The patient must understand the goal of treatment and be willing to actively participate in the exercise program.
It is important to educate the patient to avoid activities that aggravate the pain, such as sleeping on the affected shoulder or repeatedly raising the arm above the shoulder. Maintaining good general physical fitness with non-painful activities, such as walking or cycling, is also recommended.
The effects of rehabilitation are not immediate and may take weeks or months to be noticed. A crucial aspect is the patient's attitude: low expectations about the effectiveness of treatment have been found to be the strongest predictor of failure, even more so than the characteristics of the injury itself.
In some cases, therapy can be complemented with other treatments such as medication or injections.
Pendulum Exercise:
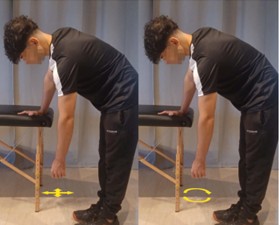
Standing or sitting in a chair, lean forward, letting your arm drop without exerting any force, so that it is perpendicular to the floor. Using your body's inertia, perform circular movements clockwise, counterclockwise, forward and backward, and to both sides. Perform 20 repetitions of each movement.
Perform:
- 20 repetitions
- 1 set
Goals:
- Relieve shoulder pain.
- Relax the surrounding muscles: shoulder, cervical, and scapular.
- Reduces shoulder stiffness and improves shoulder joint balance.
Self-Assisted Shoulder Flexion Exercise:
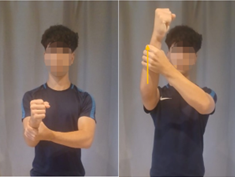
Standing or sitting. With the help of the hand of your contralateral arm, slowly move your arm forward and upward without bending your elbow. Hold for 3 seconds.
Perform:
- 10 repetitions
- 1 set
Goals:
- Shoulder pain relief.
- Reduces shoulder stiffness and improves shoulder joint balance.
- Prevents loss of mobility
Standing Posterior Capsular Stretch:
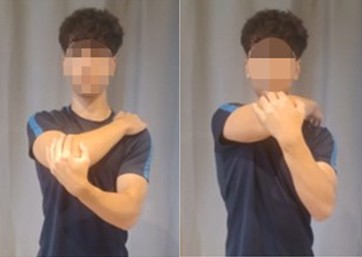
Standing. Place the assisting hand on the elbow. Bring the elbow toward the shoulder of the assisting arm until you feel a tightness.
When beginning stretches, it is crucial to avoid pain. You should stretch only until you feel tension in the muscle and tendons, and then hold that position for a while until the tension decreases. With practice, you can extend the holding time, but you should never feel pain.
Goals:
- Relieves tension in the posterior capsule and external rotators.
- Improves joint balance in internal rotation.
- Improves joint balance and shoulder stability.
Elastic Band Rowing Exercise:
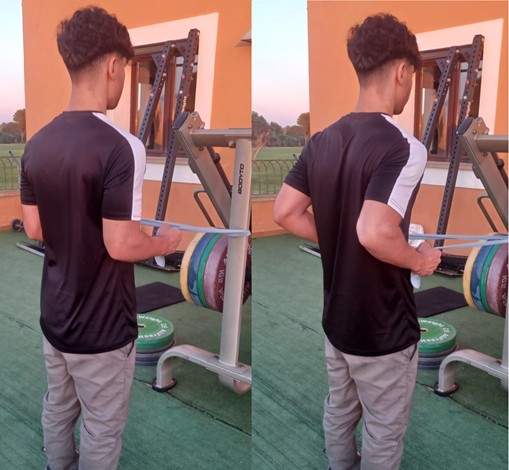

Stand facing a door or a structure that allows you to anchor the resistance band. Tie the resistance band and hold the ends with your hands. Keep your back straight. Look forward. Stretch the band, pushing your shoulders and elbows back. Hold for 5 seconds.
Perform:
- 10 repetitions
- 3 sets
Goals:
- Improve posture and thoracic spine.
- Improve shoulder and scapula stability.
Protraction Exercise with Weights:

Lying on your back, hold your arm perpendicular to the floor with a 2kg weight in your hand. Lift your shoulder off the floor and raise your arm. Hold for 5 seconds.
Perform:
- 10 repetitions
- 3 sets
Goals:
- Strengthening of the serratus anterior muscle.
- Improved scapular stability.
- Improved postural control of the shoulder and scapula.
Abduction Exercise with Elastic Band:

Standing. Use an elastic band, stepping on the foot on the side being exercised. Raise your arm without bending your elbow or wrist, without reaching parallel to the floor. Point your arm forward 30° as you raise it. Hold this position for 5 seconds.
Perform:
- 10 repetitions
- 3 sets
Goals:
- Strengthening the supraspinatus and middle deltoid muscles.
- Improve joint balance and shoulder stability.
External Rotation Exercise with Elastic Band:

Stand sideways to a door. Tie the resistance band to the doorknob and hold the end with one hand. Place a towel between your chest and arm. Keep your elbow at 90 degrees, close to your chest, and your wrist straight. Keep your back straight. Gaze forward. Stretch the band outward to about 50 degrees. Hold for 5 seconds.
Perform:
- 10 reps
- 3 sets
Goals:
- Strengthen shoulder external rotators.
- Improve joint balance and shoulder stability.
Internal Rotation Exercise with Elastic Band:

Stand sideways to a door. Tie the resistance band to the doorknob and hold the end with one hand. Place a towel between your chest and arm. Keep your elbow at 90 degrees, close to your chest, and your wrist straight. Keep your back straight. Gaze forward. Pull the band inward to about 50 degrees. Hold for 5 seconds.
Perform:
- 10 reps
- 3 sets
Goals:
- Strengthen internal rotators of the shoulder.
- Improve joint balance and shoulder stability.
External Rotation Exercise with Stick:

Stand. Grab a stick with both hands. Place a towel between your elbow and chest. Elbow at 90°. Push with your good arm and move the hand of the arm you're rehabilitating outward.
Perform:
- 10 reps
- 1 set
Goals:
- Pain relief.
- Improved anteroinferior capsular tension.
- Improved joint balance in external rotation.
Dumbbell Row Exercise:
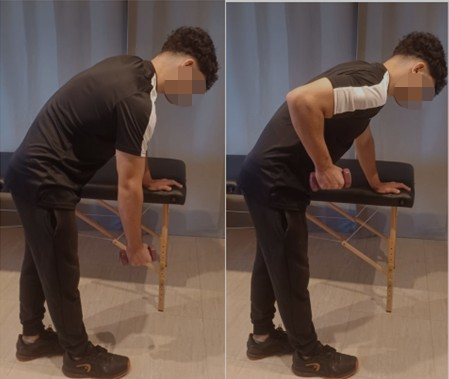
Standing. Bend forward, letting your arm drop without exerting any force, so that it's perpendicular to the floor with a 2 kg dumbbell in your hand. Bend your elbow and bring it back. Hold for 5 seconds.
Perform:
- 10 repetitions
- 3 sets
Goals:
- Relief and prevention of shoulder pain.
- Improve shoulder and scapula stability.
Internal Rotation Exercise with Dumbbell:
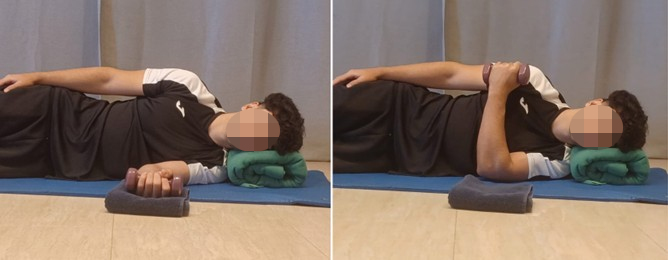
Lying on your side on the shoulder you're rehabbing. With your elbow flexed at 90° and a dumbbell in your hand, bring the dumbbell toward your body. Hold for 5 seconds.
Perform:
- 10 repetitions
- 3 sets
Goals:
- Strengthening internal rotators.
- Relief and prevention of shoulder pain.
- Improve shoulder stability.
External Rotation Exercise with Dumbbell:

Lying on your side, place a towel between your arm and chest, elbow bent at 90°, and a dumbbell in your hand. Lift the dumbbell upward. Hold for 5 seconds.
Perform:
- 10 reps
- 3 sets
Goals:
- Strengthen external rotators.
- Relieve and prevent shoulder pain.
- Improve shoulder stability.
>> DOWNLOAD THESE EXERCISES FOR SUPRASPINAUS TEAR HERE: 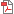 Exercises-for-supraspinatus-tear-drjordijimenez.PDF <<
Exercises-for-supraspinatus-tear-drjordijimenez.PDF <<
>> DOWNLOAD A SHOULDER EXERCISE COMPLIANCE CALENDAR HERE:  shoulder-compliance-calendar-drjordijimenez.PDF <<
shoulder-compliance-calendar-drjordijimenez.PDF <<
Book an appointment with Dr. Jordi Jiménez. He will see you at the center of Palma de Mallorca and help you regain your quality of life.

![[VIDEO] Ultrasound-guided infiltration of the lumbar facets](https://drjordijimenez.com/imagen/100/100/imagenes-pagina/sindrome-facetario-lumbar-drjordijimenez (1).jpg)
![[VIDEO] Ultrasound-guided infiltration of the hip joint](https://drjordijimenez.com/imagen/100/100/Imagenes/valgo-dinamico-rodilla-drjordijimenez.jpg)