Hip osteoarthritis
- 31/01/2023
What is hip osteoarthritis?
Hip osteoarthritis, also called coxarthrosis, is a degenerative disease that affects the hip joint. It is characterized by the progressive deterioration of the articular cartilage and underlying bone, causing pain, stiffness, and difficulty moving the joint. As the disease progresses, joint deformity and loss of mobility may occur.
Hip osteoarthritis is common in older people, but it can also occur in younger people due to previous injuries, natural wear and tear of the cartilage, or congenital problems.
What causes hip osteoarthritis?
Hip osteoarthritis occurs when the cartilage lining the hip joints wears down. This can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Aging: The natural wear and tear of the body as we age can cause hip osteoarthritis.
- Injuries: Previous hip injuries, such as a fracture or dislocation, can increase the risk of developing hip osteoarthritis.
- Joint deviations: Abnormalities in the shape of the hip joint, such as hip dysplasia, can increase the risk of hip osteoarthritis.
- Overweight: Excess weight can increase stress on the hip joints and increase the risk of hip osteoarthritis.
- Genetic disorders: Some genetic disorders can increase the risk of developing hip osteoarthritis.
- Other diseases: Diseases such as osteoporosis, rheumatoid arthritis, and lupus can increase the risk of hip osteoarthritis.
How is hip osteoarthritis diagnosed?
The diagnosis of hip osteoarthritis is based on a combination of medical history, symptoms, physical examination, x-ray images, and, in some cases, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT).
A medical history is used to determine the symptoms and their duration, as well as any history of injuries or illnesses that may be related to hip osteoarthritis. A physical examination is used to detect any pain or swelling in the hip joint, as well as any movement limitations or weakness. Hip X-rays are useful for detecting any wear or degeneration in the hip joint(Figure 1). MRI or CT are often used to obtain detailed images of the hip joint and can help identify any additional problems, such as a fracture or ligament injury.
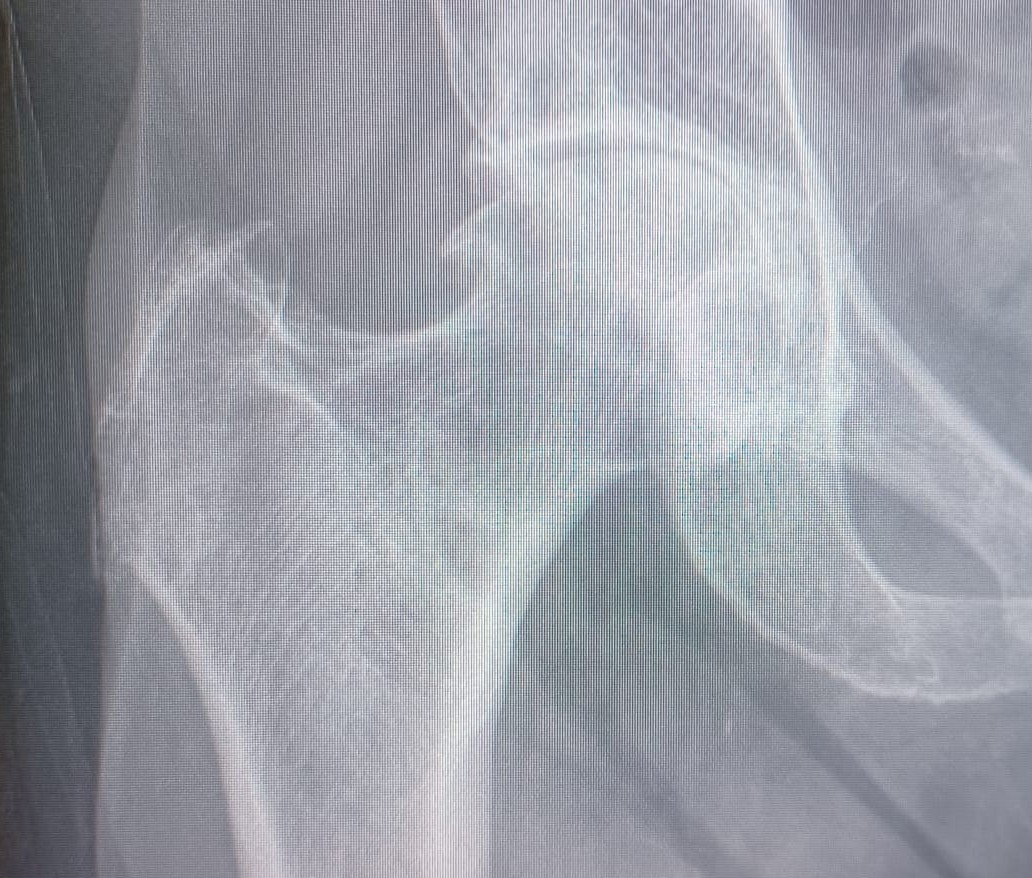
Figure 1: Hip osteoarthritis
How is hip osteoarthritis treated?
Treatment for hip osteoarthritis may include non-surgical options, such as pain relievers, anti-inflammatories, physical therapy, and strengthening exercises.
Ultrasound-guided injections for hip osteoarthritis are a medical technique used to relieve pain and inflammation in the hip joint. The procedure involves injecting an anti-inflammatory drug, hyaluronic acid, or PRP directly into the joint through a needle guided by ultrasound, allowing for greater precision. This technique is used as an adjuvant treatment for patients with hip osteoarthritis and can improve the patient's quality of life. However, it is not a cure for the disease.
If the pain caused by hip osteoarthritis is not manageable through conservative means, there are surgical options such as total hip arthroplasty (total hip replacement) or partial hip arthroplasty (partial hip replacement).
The appropriate treatment will depend on the severity of the disease and the patient's needs and preferences. It's important to mention that prevention and weight control are essential to delaying the progression of the disease.
Make an appointment with Dr. Jordi Jiménez. He will see you in the center of Palma and help you regain your quality of life.

![[VIDEO] Ultrasound-Guided Injection for Trigger Finger](https://drjordijimenez.com/imagen/100/100/Imagenes/infiltracion-ecoguidada-dedo-resorte-drjordijimenez.jpg)
![[VIDEO] Ultrasound-guided infiltration of the lumbar facets](https://drjordijimenez.com/imagen/100/100/imagenes-pagina/sindrome-facetario-lumbar-drjordijimenez (1).jpg)
![[VIDEO] Ultrasound-guided infiltration of the hip joint](https://drjordijimenez.com/imagen/100/100/Imagenes/valgo-dinamico-rodilla-drjordijimenez.jpg)