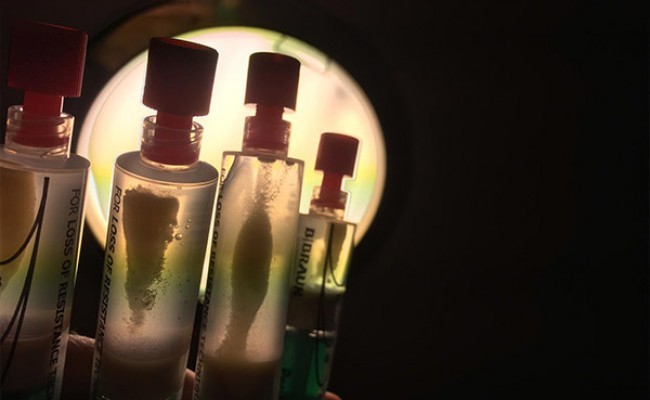
Percutaneous treatment of calcific tendonitis (Barbotage Technique)
- 13/02/2019
What is the barbotage technique?
Barbotage is an ultrasound-guided technique that allows for the drainage of calcific material from calcific rotator cuff tendinopathies.
There are different percutaneous techniques for the treatment of calcific tendonitis, all based on puncture of the calcification to fragment it and aspirate its calcium content. Previously, fluoroscopy-guided needle aspiration was considered an elective technique.
Why is ultrasound used in the barbotage technique?
Several authors have proposed ultrasound guidance as an effective modality to avoid radiation exposure from fluoroscopy, while allowing us to pinpoint the specific location of the calcification. Therefore, a prior ultrasound examination is necessary to locate it.
What if there are multiple calcifications in different rotator cuff tendons?
If there are multiple calcifications, the procedure will focus on the largest ones or those most clearly related to the patient's symptoms. The spontaneous resolution of calcium deposits means that these deposits do not require treatment.
Does barbotage require hospitalization?
No. Barbotage is performed on an outpatient basis and does not require hospitalization.
How is barbotage performed?
The procedure can be performed with the patient sitting or supine; the latter position is preferable for calcifications in the subscapularis tendon or in patients with a history of vagal syncope.
Local anesthetic is administered intrabursally and along the surface of the bursa of the affected tendon. Next, we puncture the calcification with the same anesthetic needle and check the needle positioning in long and short axis views. Already in the long axis, we proceed to change the syringe for another one filled with saline solution and begin a sequence of short pressures and releases with the syringe plunger.
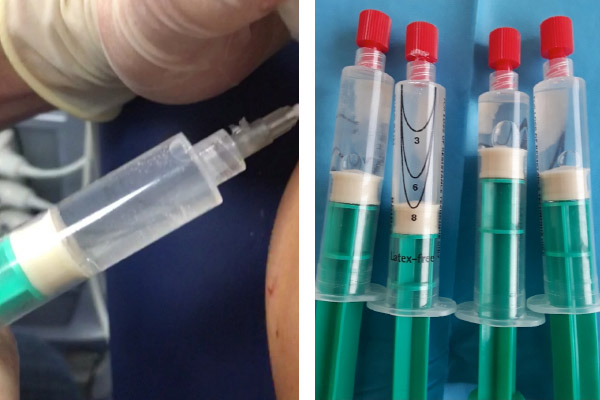
During this procedure, the extraction of calcium fragments is observed, creating turbidity in the saline solution and gradually precipitating in the syringe itself. Simultaneously, a cavity appears in the calcification, which expands upon compression and shrinks when the pressure is released. Lavage should be discontinued when calcium extraction ceases. Occasionally, the needle may become clogged during the procedure, especially during the first punctures of the calcification. Several syringe changes with clean saline solution are often necessary to monitor continued calcium extraction.
Does the patient experience pain after barbotage?
No. At the end of the final lavage, we will infiltrate the subacromiodeltoid bursa with local anesthetic plus a corticosteroid to control pain caused by the release of calcium into the bursa during the first few days after the procedure.

Is a single Barbotage session definitive?
It depends on the type of calcification and the amount of material drained. Occasionally, more than one session is required, and generally more than one corticosteroid injection to control subsequent pain due to the spontaneous and continuous release of calcium into the shoulder bursa.
What changes are expected in tendon calcification after barbotage, and how long are these changes typically observed?
After barbotage, a significant reduction or partial/total disappearance of calcification is expected in the following weeks or months. Initially, fragmentation or dispersion of the calcification may be observed in the first few days. Progressive resorption is usually evident by ultrasound or radiography within 4 to 12 weeks, although in some cases it can last up to 6 months. Clinical improvement (reduction in pain and increased mobility) generally precedes complete resolution of the calcification.
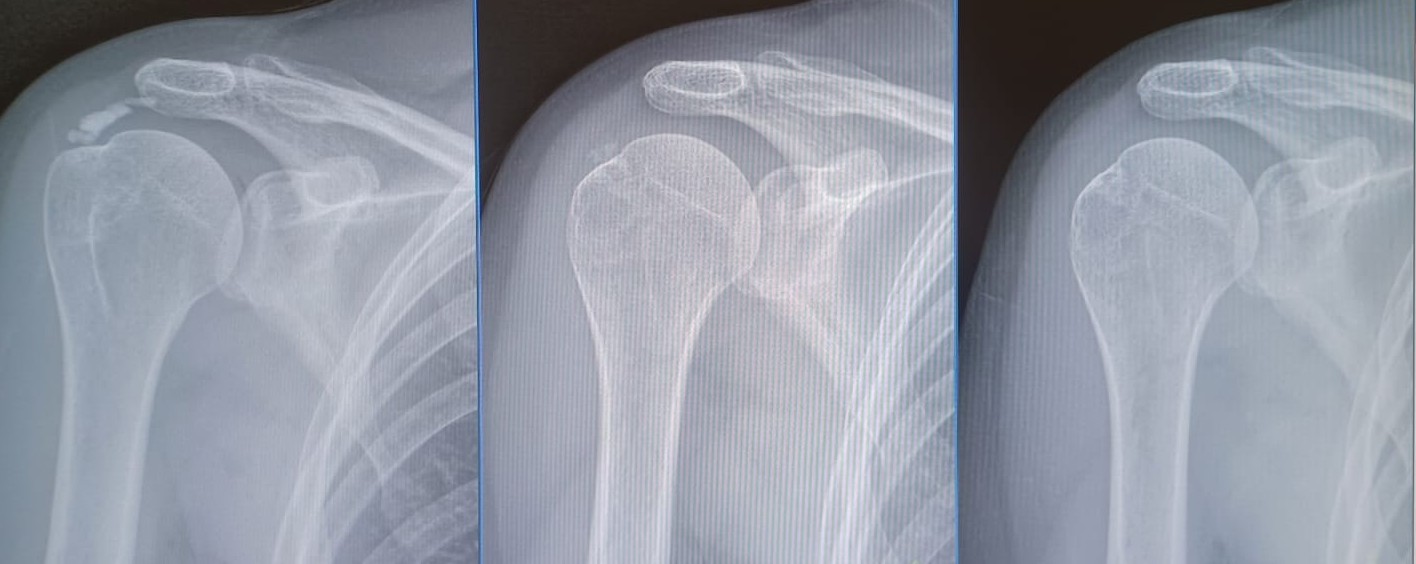
Evolutionary changes in calcification of the supraspinatus tendon after performing the barbotage technique
Make an appointment with Dr. Jordi Jiménez. He will see you in the center of Palma and help you regain your quality of life.

![[VIDEO] Ultrasound-Guided Injection for Trigger Finger](https://drjordijimenez.com/imagen/100/100/Imagenes/infiltracion-ecoguidada-dedo-resorte-drjordijimenez.jpg)
![[VIDEO] Ultrasound-guided infiltration of the lumbar facets](https://drjordijimenez.com/imagen/100/100/imagenes-pagina/sindrome-facetario-lumbar-drjordijimenez (1).jpg)
![[VIDEO] Ultrasound-guided infiltration of the hip joint](https://drjordijimenez.com/imagen/100/100/Imagenes/valgo-dinamico-rodilla-drjordijimenez.jpg)