Rhizarthrosis
- 03/02/2023
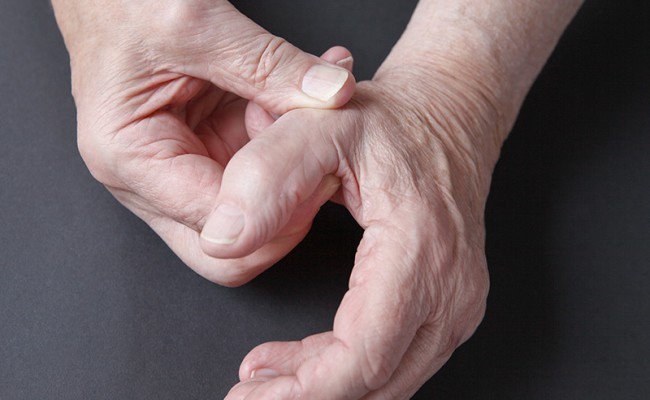
What is rhizarthrosis?
Rhizarthrosis is a degenerative condition of the joint at the base of the thumb, also known as the trapeziometacarpal joint. It is a form of osteoarthritis, a disease characterized by the wear and tear and loss of cartilage in a joint. Rhizarthrosis occurs when the cartilage in the joint wears away, causing pain, swelling, and difficulty moving the thumb.
What are the causes of rhizarthrosis?
Causes of rhizarthrosis include:
- Age: Cartilage wear is a natural process that occurs over time, so rhizarthrosis is more common in older people.
- Genetic predisposition: There is a hereditary component, so having a family history of osteoarthritis increases the risk.
- Previous injuries: Trauma, such as fractures or sprains to the thumb or wrist joint, can damage the cartilage and predispose to the development of rhizarthrosis in the future.
- Rheumatic diseases: Rheumatic diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, can affect the joint at the base of the thumb and contribute to rhizarthrosis.
- Overuse: Overuse of the joint at the base of the thumb, such as in sports that require repetitive hand movements or in jobs that involve the use of hand tools, can wear down the cartilage and increase the risk of rhizarthrosis.
How is rhizarthrosis diagnosed?
The diagnosis of rhizarthrosis is based on the patient's medical history and symptoms, as well as the results of various tests and examinations. Some of the tests and exams that may be used to diagnose rhizarthrosis include:
- Physical exam: The doctor will examine the joint at the base of the thumb to assess pain, inflammation, and mobility.
- X-ray: An X-ray can show cartilage wear and osteophyte formation.
- MRI: These imaging tests can provide detailed images of the joint at the base of the thumb and can show any damage to the cartilage or bones.
How is rhizarthrosis treated?
Treatment for rhizarthrosis focuses on relieving pain and improving the function of the joint at the base of the thumb. Treatments may include:
- Physical therapy: Physical therapy can help improve joint mobility and strength. The physical therapist can teach specific exercises to strengthen the hand muscles and reduce inflammation.
- Medications: Your doctor may prescribe analgesics to relieve pain and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to reduce inflammation.
- Ultrasound-guided injections: Corticosteroid and local anesthetic injections may be used to reduce inflammation and relieve pain. Ultrasound is recommended for injections, as it improves the accuracy and likelihood of treatment success.(See article and VIDEO about ultrasound-guided infiltration of rhizarthrosis).
- Splints and orthotics: Wearing a wrist brace or thumb splint can help reduce stress on the joint at the base of the thumb and relieve pain.
- Surgery: In severe cases or those refractory to conservative treatment, surgery to repair or replace the joint at the base of the thumb may be considered.
- Lifestyle changes: It is important to avoid activities that can put stress on the joint, such as lifting heavy objects or performing repetitive hand movements.
Book an appointment with Dr. Jordi Jiménez. He will see you at the center of Palma de Mallorca and help you regain your quality of life.

![[VIDEO] Ultrasound-Guided Injection for Trigger Finger](https://drjordijimenez.com/imagen/100/100/Imagenes/infiltracion-ecoguidada-dedo-resorte-drjordijimenez.jpg)
![[VIDEO] Ultrasound-guided infiltration of the lumbar facets](https://drjordijimenez.com/imagen/100/100/imagenes-pagina/sindrome-facetario-lumbar-drjordijimenez (1).jpg)
![[VIDEO] Ultrasound-guided infiltration of the hip joint](https://drjordijimenez.com/imagen/100/100/Imagenes/valgo-dinamico-rodilla-drjordijimenez.jpg)