Sacroiliac joint dysfunction
- 01/03/2023
What is sacroiliac joint dysfunction?
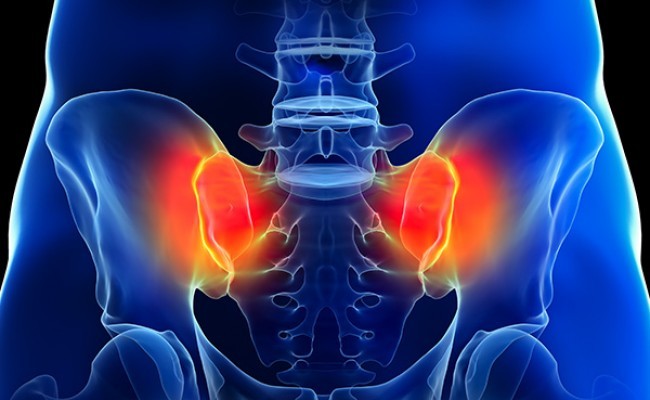
Sacroiliac joint dysfunction refers to the presence of pain in one or both sacroiliac joints.
The sacroiliac joints are the junctions between the sacrum and the ilium, and are located at the bottom of the spine.
This joint is essential for the stability and function of the pelvic area and is composed of a series of ligaments and muscles that allow limited movement. It is a joint that is fibrous on its upper part and synovial on its lower part, which means it is covered by articular cartilage and has a joint capsule that contains synovial fluid.
Where is the pain located in sacroiliac joint dysfunction?
Sacroiliac dysfunction can cause pain in the lower back, hips, and legs (see figure 1) and may be the result of injury, excessive strain, or muscle imbalance.
What are the causes of sacroiliac joint dysfunction?
Sacroiliac dysfunction can be caused by several factors, including:
- Traumatic injuries: A direct injury to the lower back, pelvis, or hip, such as a fall, car accident, or sports injury, can damage the sacroiliac joint and cause pain.
- Different leg lengths: Different leg lengths (leg length discrepancy) can alter the biomechanics of the sacroiliac joints and cause pain at this level.
- Joint wear and tear: Osteoarthritis can also affect the sacroiliac joint. Wear and tear at this joint can cause pain, stiffness, and limited movement.
- Pregnancy: During pregnancy, hormones can soften the ligaments in the pelvis, which can cause pain in the sacroiliac joint and pelvis.
- Overload: Overload on the sacroiliac joint can lead to pain. This can be caused by intense physical activity or a sudden increase in physical activity.
- Inflammatory or rheumatic diseases: These can cause selective inflammation of this joint, resulting in pain and functional limitation.
- Lumbar arthrodesis: Patients with a previous lumbar fixation may develop sacroiliac pain due to overloading these joints.
How is sacroiliac joint dysfunction diagnosed?
The diagnosis of sacroiliac joint dysfunction can be difficult, as the pain can be similar to that of other conditions of the spine and pelvis. The diagnosis of sacroiliac joint dysfunction is based on:
- History: The doctor will ask about the symptoms, duration and intensity of the pain, as well as any events or activities that may have triggered the pain.
- Physical examination: Physical tests to assess range of motion, muscle strength, and the presence of tender points.
- X-rays: X-rays can help detect abnormalities in the structure of the sacroiliac joint.
- CT scan or MRI: These imaging tests can provide a detailed view of the sacroiliac joint and can help detect any injury or inflammation.
- Ultrasound-guided local anesthetic injection: If your doctor suspects the pain is related to the sacroiliac joint, they may perform an ultrasound-guided injection of local anesthetic into the joint to determine if the pain temporarily resolves after the injection.
In some cases, additional testing may be necessary to rule out other causes of pain in the pelvis or spine.
How is sacroiliac joint dysfunction treated?
Treatment for sacroiliac joint dysfunction is primarily conservative.
- Drug treatment:
- Analgesics and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Such as ibuprofen or naproxen, can help relieve pain and inflammation.
- Muscle relaxants: These may be prescribed to reduce muscle spasms.
- Biologic medications: In cases like ankylosing spondylitis, biologic medications can be used to reduce inflammation.
- Physical therapy and exercise:
- Strengthen the muscles around the sacroiliac joint, improve flexibility, and correct postural habits.
- Low-impact exercises, such as stationary biking or water aerobics, are also beneficial.
- Specific exercises may include piriformis muscle stretches and core strengthening (abdomen and glutes).
- Ultrasound-guided injections:Ultrasound-guided injections of corticosteroids and local anesthetics directly into the sacroiliac joint can provide significant relief from pain and inflammation.
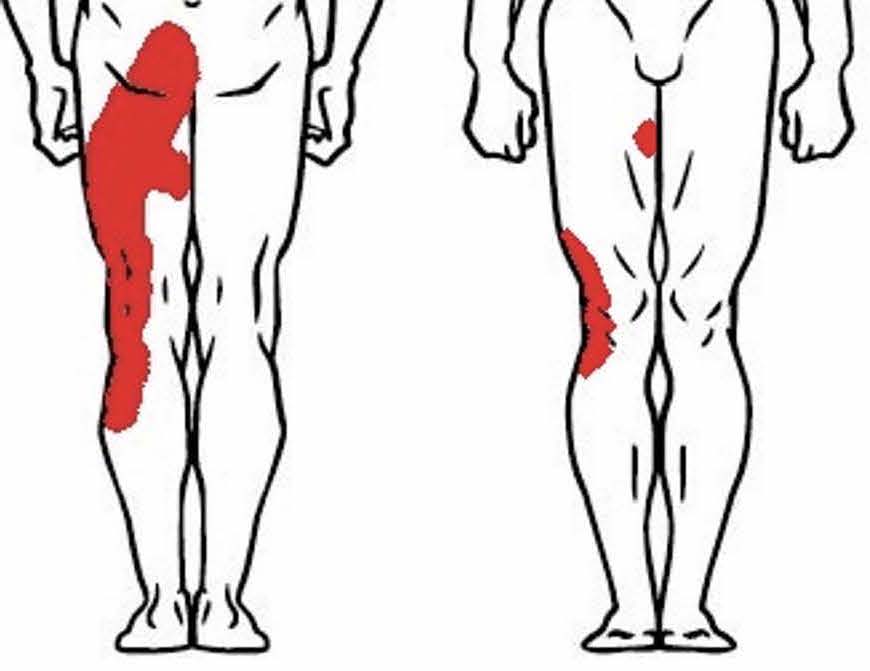
Figure 1: Referred pain pattern in lower extremities of sacroiliac joint dysfunction
Book an appointment with Dr. Jordi Jiménez. He will see you at the center of Palma de Mallorca and help you regain your quality of life.

![[VIDEO] Ultrasound-Guided Injection for Trigger Finger](https://drjordijimenez.com/imagen/100/100/Imagenes/infiltracion-ecoguidada-dedo-resorte-drjordijimenez.jpg)
![[VIDEO] Ultrasound-guided infiltration of the lumbar facets](https://drjordijimenez.com/imagen/100/100/imagenes-pagina/sindrome-facetario-lumbar-drjordijimenez (1).jpg)
![[VIDEO] Ultrasound-guided infiltration of the hip joint](https://drjordijimenez.com/imagen/100/100/Imagenes/valgo-dinamico-rodilla-drjordijimenez.jpg)